CT Scan or MRI scan - Differences, Safety and When you will need them

CT SCAN OR MRI SCAN ?
What is CT scan – Uses, Procedure, Safety and When to do it Whatis MRI scan – Uses, Procedure, Safety and When to do it What isUltrasound scan – Uses, Procedure, Safety and When to do itUltrasound scan – Recommmendations during Pregnancy CTscan – Radiation risks Aarthi scans cost What is contrast study inCT and MRI and what are the side effects..
CT SCAN OR MRI SCAN
Differences, Safety and When you will need them
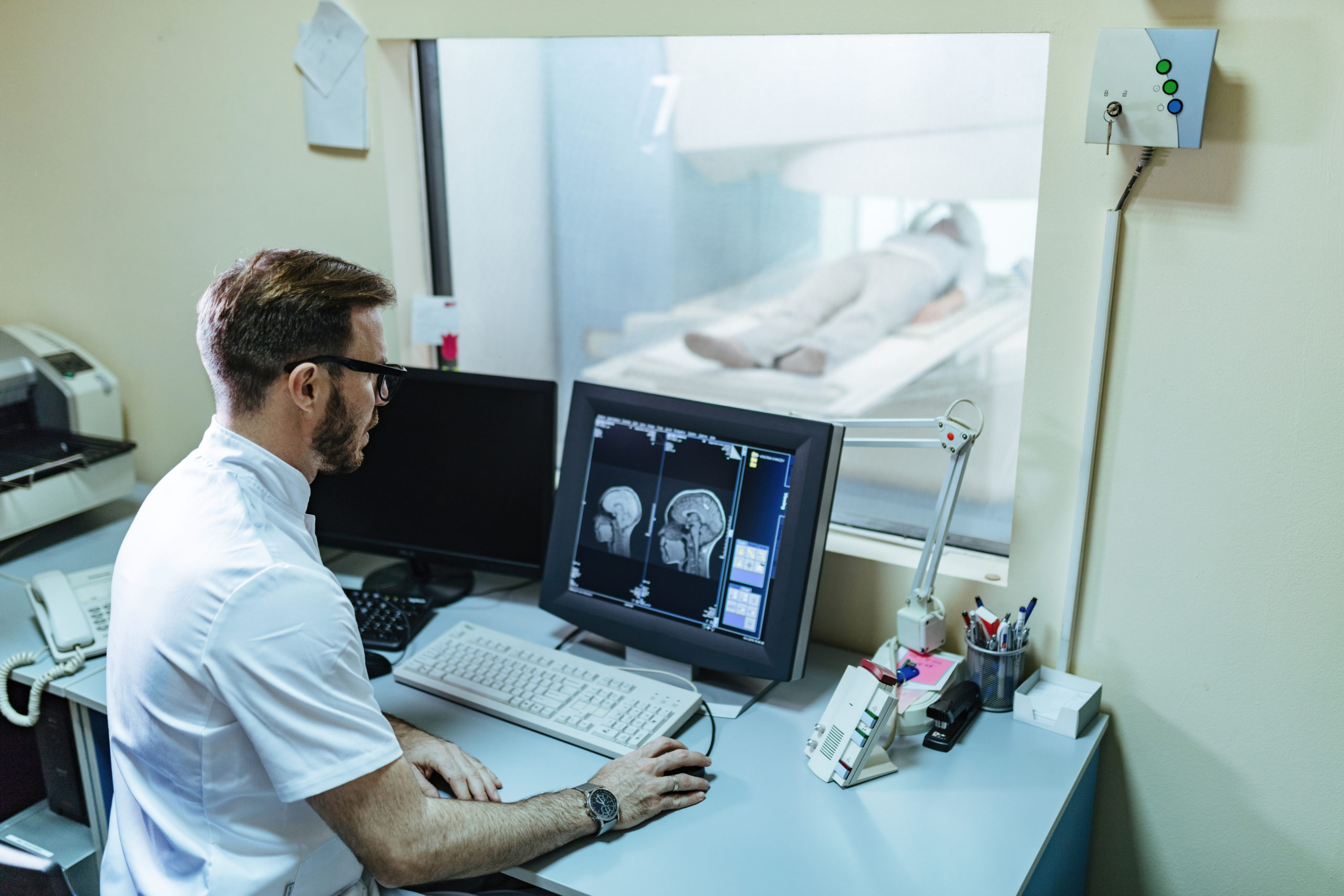
With increasing use of scanning to diagnose diseases accurately,every person comes across this question atleast once in their life.This article explains how CT scan and MRI scan work, what are the side effects, when you will need these scans, what is the difference between CT scan and MRI scan and also the cost to take CT or MRI scan.
Similarities & Differences
Similarities
Both CT and MRI scans can detect how organs inside your body look without even touching you. Yes,there was once a time when doctors needed to cut open patients just to know what was going oninside them. Thank God, times have changed. Sometimes, a radiologist or your doctor may request acontrast study (where they inject a medicine through your arms) in both CT and MRI scans, if they wanta more accurate diagnosis (Infection vs Tumor, Benign tumor vs Malignant tumor, Spread of infectionor tumor etc.,)
Differences
A CT scan machine uses Xrays and MRI scan machine uses magnetism to scan your body. Click here for a complete description of how a CT scan works and how a MRI scan works. A CT scan may take around 1 to 5 minutes for actual scanning, while a MRI scan takes around 10 to 20 minutes of scanning time. Generally a MRI scan causes more noise than a CT machine (Better get your own earplugs or ask for cotton balls to stuff your ears). A CT scan has a smaller length gantry (that round hollow thing into which your body goes inside) than MRI, so the chances of getting claustrophobia are more in MRIs.Click here to know how to avoid clautrophobia in MRI scan. Since CT scan emits Xrays to scan your body, there is a risk of radiation to your body. Radiation may cause cancer, and I stress MAY CAUSE cancer. There is no clear data as of now, as to how much radiation or how many CT scans can cause cancer. It is postulated that too many CT scans in a short span of years or in a young age can cause cancer without concrete proof. Click here for A detailed article on CT and Radiation risks. A MRI scan uses no radiation and magnetism does not cause any side effects. The reason why still more CT scans are taken is, benefits of diagnosing a disease with CT scans outweigh the harm caused by radiation risk.
CT SCAN OR MRI SCAN –
When you will need them
But the main deciding factor on whether you will need a CT or MRI scan is not the radiation risk or scanning time, its what you are suffering from and what the physician, radiologist think is a better modality to diagnose your suspected condition. Since CT and MRI use different physical ways to scan your body, the images produced by them are different and a few body parts are better depicted in only CT or MRI. Below are a few broad classifications and I want to stress that every patient and every disease is unique and your clnician, radiologist is the best deciding authority on which scan you need depending on the suspected disease.
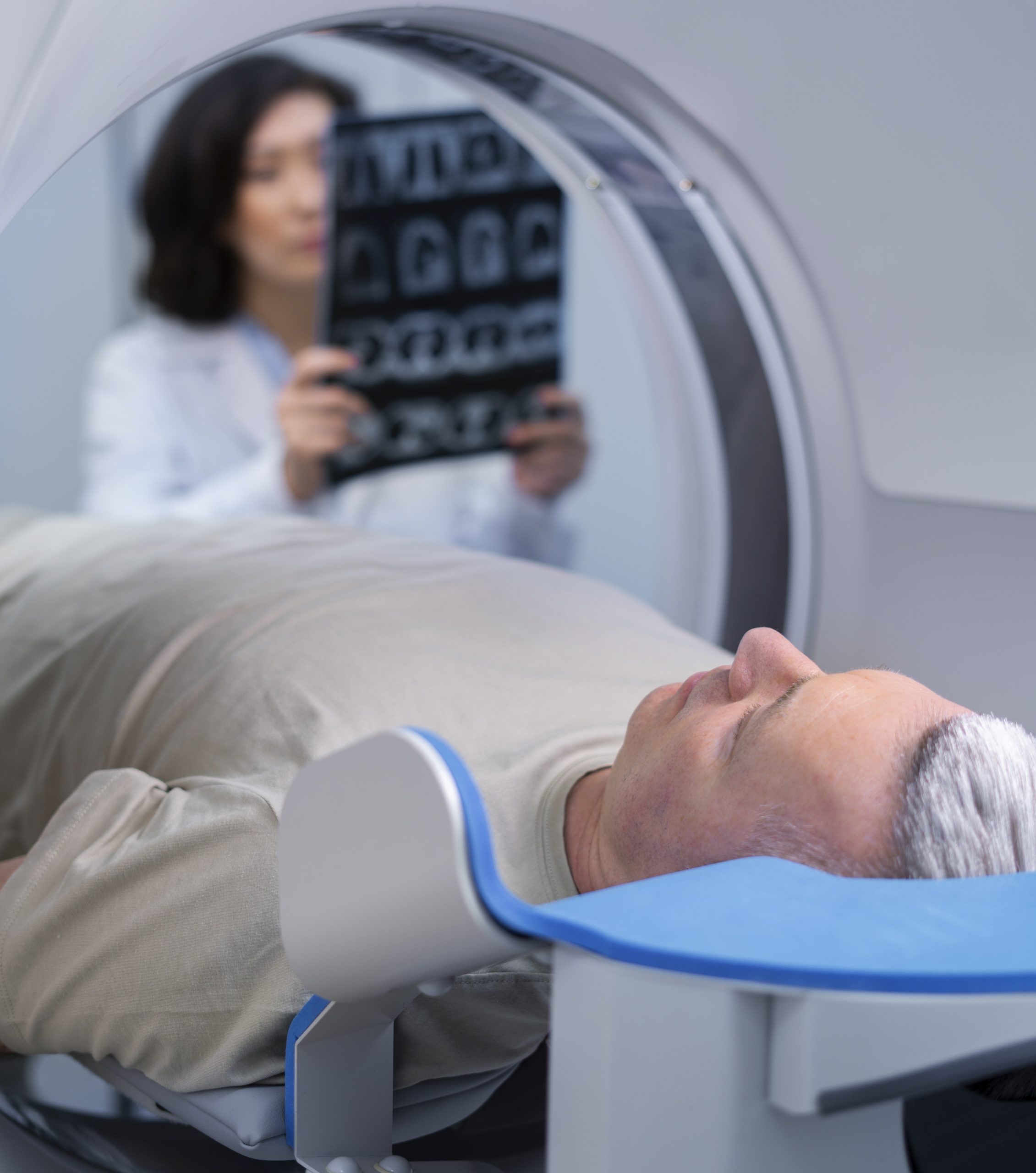
| Brain | MRI is the best modality and is more specific and sensitive than CT. A clinicianmay ask for a CT scan during emergency situations like stroke, head injury andwhen the patient cannot lie still in MRI for 10 minutes. |
| Chest | CT is the best modality to image lungs and mediastinum (the space betweenthe lungs where heart, major vessels and food pipe travel). MRI is the bestmodality to image breasts and chest wall. |
| Heart | To see the arteries supplying your heart muscles and wheter there is any blockin them, Cardiac CT or CT coronary angiogram are used (both are the same).Cardiac MRI can show your heart beating in real motion which a CT scan cannotdo and hence used to diagnose heart muscle dysfunction and contractile function. |
| Kidney or ureter stones | CT is the only modality that shows the stones clearly and doesn't miss any. |
| Small and large intestine | CT with oral contrast (where you have drink around 1 liter of water mixed with amedicine) is better than MRI. However a physician may ask for a MRI scan if hethinks you may need multiple time scannning. |
| Uterus and Ovary | MRI is far superior than CT in imaging diseases of uterus and ovaries. |
| Liver, Pancreas, Gallbladder, Spleen | Too many variables and diseases, entirely a physician / radiologist opinion onwhether to do CT or MRI. |
| Joints | MRI is far superior than CT in imaging diseases in and around joints. Only whenfractures are suspected and a physician requires to get a 3D view the bones tobe operated, he may ask for a CT. |
| Arteries in neck, chest,abdomen, arms and legs | CT angiogram (with contrast) is routinely used. MRI Angiogram (without contrast)can be used in renal failure patients and in patients with contrast allergy. |
| Pregnant patients | CT is contraindicated (not adviced) due to radiation risk to the baby. MRI scan isusually used in pregnant patients to scan the mother or the baby if required. |
| Pus discharge or abscessaround anal region | MRI Fistulogram is routinely used. CT Fistulogram requires injection of contrastthrough the discharging opening and may be painful. I stress once again, theseare the general recommendations for these broad categories and each patientis unique and may be offered CT or MRI depending on their condition. |
CT SCAN AND MRI SCAN – COST
The following are the prices in our Aarthi scans and labs. We are the most affordable diagnostic service provider in India and transparency is our motto. As a routine, we charge lesser
- Cost of MRI scans – Rs 4000 per study
- Cost of CT scans in night – Rs 1000 to Rs 2000 per study
- Cost of MRI scans in night – Rs 2500 per study


